About OCR
OCR is an abbreviation for Optical Clear Resin.
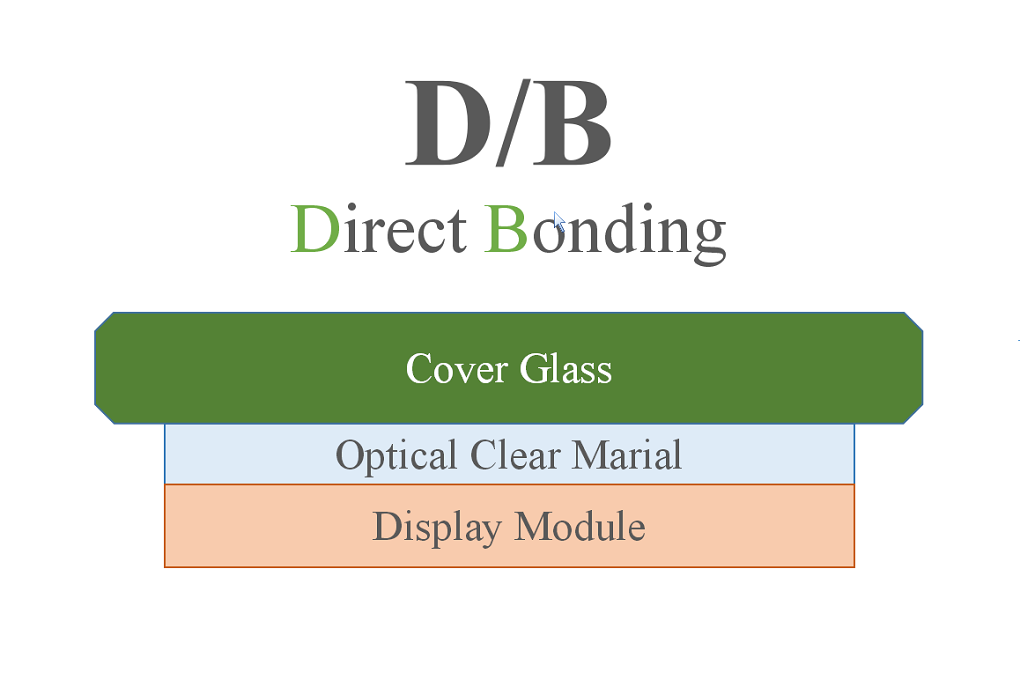
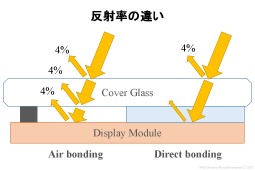
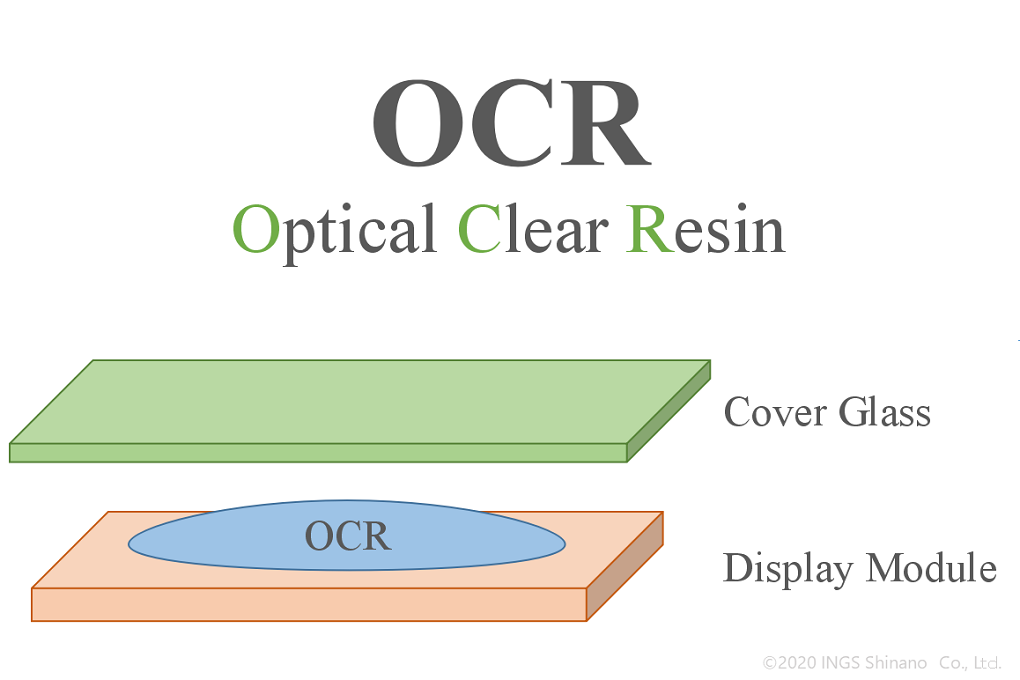
If there is an air layer between the display and the cover glass / touch panel, etc., the appearance will deteriorate due to interfacial reflection. To improve its appearance (to reduce interfacial reflection), the space is filled with a material with a refractive index close to that of the material to be bonded. OCR is one of the materials that fills the space.
For details, see "About direct bonding".
Features of OCR
OCR is initially liquid. At the time of laminating, OCR is applied to the panel and then laminated to the opposite panel.
The merit for OCA is that if there is any misalignment or foreign matter at the time of laminating, it is easy to rework if it can be found before curing. Also, compared to OCA, the material cost seems to be cheaper because there is no sheet processing or outer cut.
In addition, since it is filled with liquid, it can absorb different shapes as well as printing steps on the cover glass.
However, since it is a liquid material, care must be taken when handling it. In particular, it is known that if it gets into the gap of a material that you do not want to enter when it is uncured, it will cause problems such as display problems later.
About the process
In the OCR method, a liquid is applied to one panel and the opposite panel is brought closer to bond.
Many OCRs are designed to cure with UV (ultraviolet) light, so a spot light source cures the resin (temporary cure). After that, UV is applied to the entire surface to promote the reaction as a whole and bond.
In addition, there are many variations such as two-component curing type, thermosetting type, and combined type of each.
Ings Shinano has a long track record of handling a wide variety of OCRs.
Please feel free to contact us.