Mini LED lighting board part 1
We started a technical blog.
We would like to introduce a concrete example using Ings Shinano's technology.
However, we are basically a contract processor, and the products we work on every day are confidential to our customers, so we cannot introduce them as they are.
Therefore, we would like to introduce the exhibition samples made for the exhibition and the processing performed for internal evaluation to the extent that they can be disclosed.
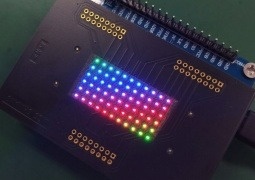
First of all, we will introduce the lighting board used for the mini LED exhibition and an example of mounting the mini LED.
The following is an explanation of the exhibits.


There is a sample in which RGB individual LEDs are arranged to form a matrix, and a sample in which Blue LEDs are arranged at a pitch of 0.2 mm.
The LEDs installed in both are 0.2 x 0.1 mm size (0201MM) mini LEDs. The small capacitor and resistor chip parts are 0.4 x 0.2 mm (0402MM), which is 1/4 the size, so you can see how small they are.
You can't pinch it with ordinary tweezers, and if you drop it somewhere, you can't find it. Even with chip capacitors, 0603 size requires some getting used to soldering by hand, but 0201 size is probably not possible.
By the way, as I mentioned earlier, we are a company that provides implementation services.
We have made it possible to bond mini LEDs by introducing a bonder that supports mini LEDs, but how to use this is basically up to the customer. We don't have much know-how to turn on LEDs in the company, so we have been thinking about ways to appeal how to use mini LEDs by groping.
First, the RGB matrix.
When we realized that we could get three types of LED emission colors, R, G, and B, the idea of "let's shine the three colors of RGB" came up immediately.
The problem is how to make it shine.
At best, it was at the level of attaching a current limiting resistor and turning it on individually, and wondering if matrix operation could be performed with a microcomputer + shift register, but the mini LED is small. There was also a desire to turn on as many lights as possible, so we continued to research various ways to turn them on.
We found an LED drive IC there. It was an IC that could control 18x11 matrix LEDs with one chip.
(Continued to Part 2)